[ad_1]
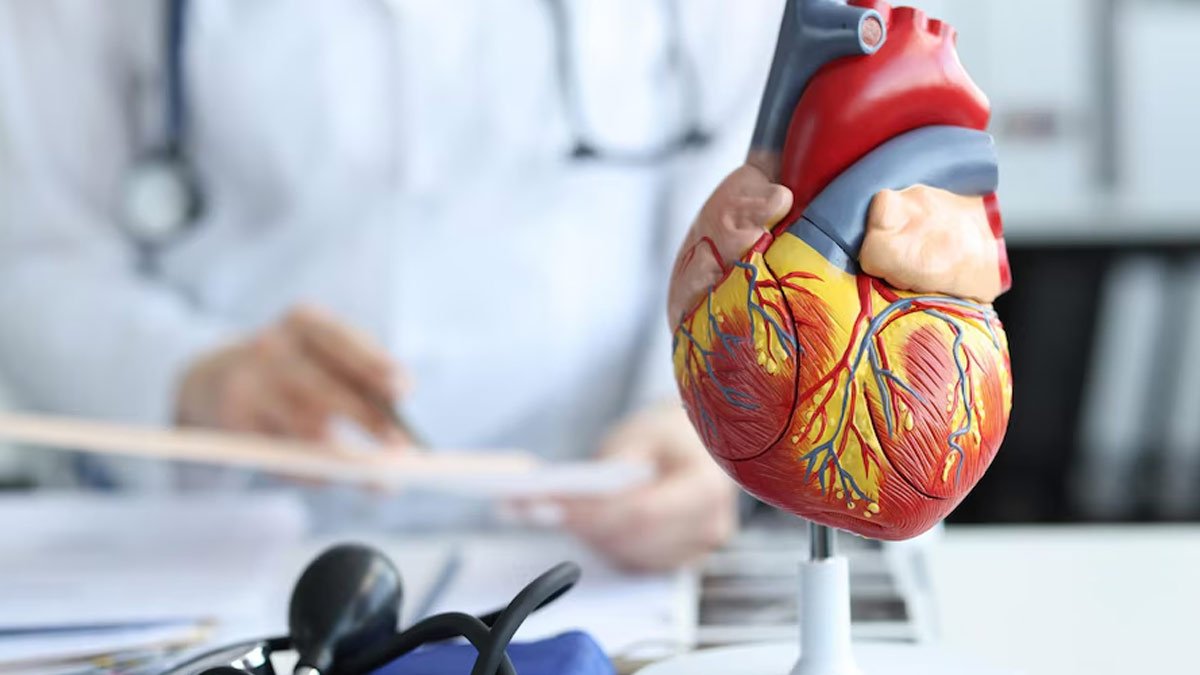
- Heart failure is a serious condition in which the heart loses its ability to pump enough blood throughout the body.
- Certain lifestyle choices, including diet, can influence a person’s risk of heart failure, and researchers are interested in understanding what factors can protect against heart failure. Masu.
- One study found that higher adherence to the EAT-Lancet diet, which focuses on plant-based foods while limiting sugar and animal foods, was associated with a lower risk of heart failure.
Heart failure remains a serious disease, affecting millions of people in the United States alone. Prevention is a key component of heart failure management strategies.
New research published in JACC: Heart failure investigated the effects of certain diets on heart failure. In an analysis of more than 23,000 participants with a median follow-up of 25 years, researchers found greater adherence to a specially designed diet rich in plant-based foods (called the EAT-Lancet diet). found that doing so seems to help reduce the risk of heart disease. Failure.
The researchers also identified key proteins associated with heart failure and inversely correlated with the EAT-Lancet diet.
be
it might be a big deal
“It’s important to note that this is not the case,” said Majid Basit, M.D., a cardiologist at Memorial Hermann in Houston who was not involved in the current study. Today’s medical news This shows that heart failure can have a serious impact on a person’s life.
“Heart failure affects 6.7 million Americans over the age of 20. Almost 25% of Americans will develop heart failure in their lifetime. This condition affects the ability to perform simple household tasks such as walking to the mailbox. It also frequently leads to hospitalization and death. We spend nearly $60 billion each year to treat heart failure.”
Because heart failure poses a significant burden, preventing heart failure when possible is a positive step towards the health of individuals and communities. As the study authors note, dietary changes are one intervention that may help limit the number of heart failure cases.
This particular study was a Swedish population-based cohort study and included 23,260 participants. Researchers excluded participants who had a history of other heart-related health events, stroke, previous heart failure, or cancer at baseline.
The average age of participants was less than 58 years. Median follow-up was 25 years, allowing sufficient examination of long-term health outcomes.
Researchers examined whether participants adhered to the EAT-Lancet dietary indicators.
The EAT-Lancet diet focuses on plant-based food sources, but with a greater emphasis on ingredients such as legumes and grains than the Mediterranean diet. However, it still encourages adequate intake of fruits and vegetables. Also, rather than eliminating animal food sources, just limit animal foods and reduce sugar-rich foods.
Karen Z. Berg, MS, RD, a registered dietitian who was not involved in the study, further elaborated. MNT:
“The EAT-Lancet diet emphasizes plant-based foods, but is not necessarily a completely vegan or vegetarian diet. It emphasizes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, fish, legumes, nuts, unsaturated oils, and Limit potatoes, dairy products, beef, lamb, pork, poultry, eggs, and added sugars.Many of the foods restricted in this diet have long been known to have a significant impact on heart disease and heart failure. It was.”
Based on the participants’ dietary ratings, the researchers divided the participants into five groups depending on how closely they followed the EAT-Lancet dietary indicators. The researchers ran three different analytical models, taking into account various covariates such as age, gender, and total energy intake.
During the study period, 1,768 participants developed heart failure.
Overall, the researchers found that increased adherence to the EAT-Lancet dietary index was associated with decreased risk of heart failure.
When researchers looked at individual dietary components, they found that eating more fruit and unsaturated oils was associated with a lower risk of heart failure, and that moderate dairy intake at baseline was associated with lower risk of heart failure. found that dairy intake was associated with a lower risk of heart failure compared to dairy intake.
Berg said:[i]It is interesting […] Fruit intake and unsaturated oil intake appear to have the most positive effect in reducing the incidence of heart failure. ”
“Fruits are rich in phytonutrients, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, so this is another good reason to ‘eat the rainbow,'” she told us. “Unsaturated oils contain so-called ‘healthy fats,’ and this study further proves the protective effects of omega-3 and omega-6. Foods high in unsaturated fats include olive oil, Contains nuts, seeds and fish.
The researchers were also able to test specific plasma proteins in 4,742 participants. They looked at how these proteins were associated with heart failure risk and the EAT-Lancet dietary index.
Ultimately, they identified eight plasma proteins associated with both components. They noted that these proteins “provide information on potential pathways mediating such an association,” meaning an association between the EAT-Lancet diet and heart failure.
“This study looked at the EAT-Lancet diet, which encourages eating healthy foods such as whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and fish, and avoiding foods with red meat, saturated fat, and added sugar. Such a diet has positive health effects, including lower blood pressure, lower cholesterol, and a more ideal body weight. This study shows that a healthy diet can reduce cases of heart failure. We have shown that,” Baijit said.
Despite the practical and encouraging findings of recent research, it is also important to recognize its limitations.
First, the authors note that they only collected one baseline dietary measure. This means we were unable to see how participants’ dietary intake changed during the follow-up period. Some data relied on participant reporting, which may have influenced the results.
Second, researchers may not have examined all important plasma proteins associated with the EAT-Lancet diet, so future studies could expand in this area.
This study is also observational and cannot prove cause and effect. The researchers further acknowledged the risk of residual confounding and the fact that the study population was predominantly white. Future studies should also include other population groups to examine the association between diet and heart failure risk in different populations.
As research continues to identify the best diets to prevent heart failure, doctors can help their patients make food choices that are most beneficial for heart health.
Chen-Han Chen, MD, a board-certified interventional cardiologist and medical director of the Structural Heart Program at MemorialCare Saddleback Medical Center in Laguna Hills, California, who was not involved in the study, said: states. “This study adds to many other previous studies” that link a healthy plant-based diet to improved cardiovascular disease. Future research should focus on identifying techniques to promote heart-healthy dietary intake in the general population. ”
[ad_2]
Source link